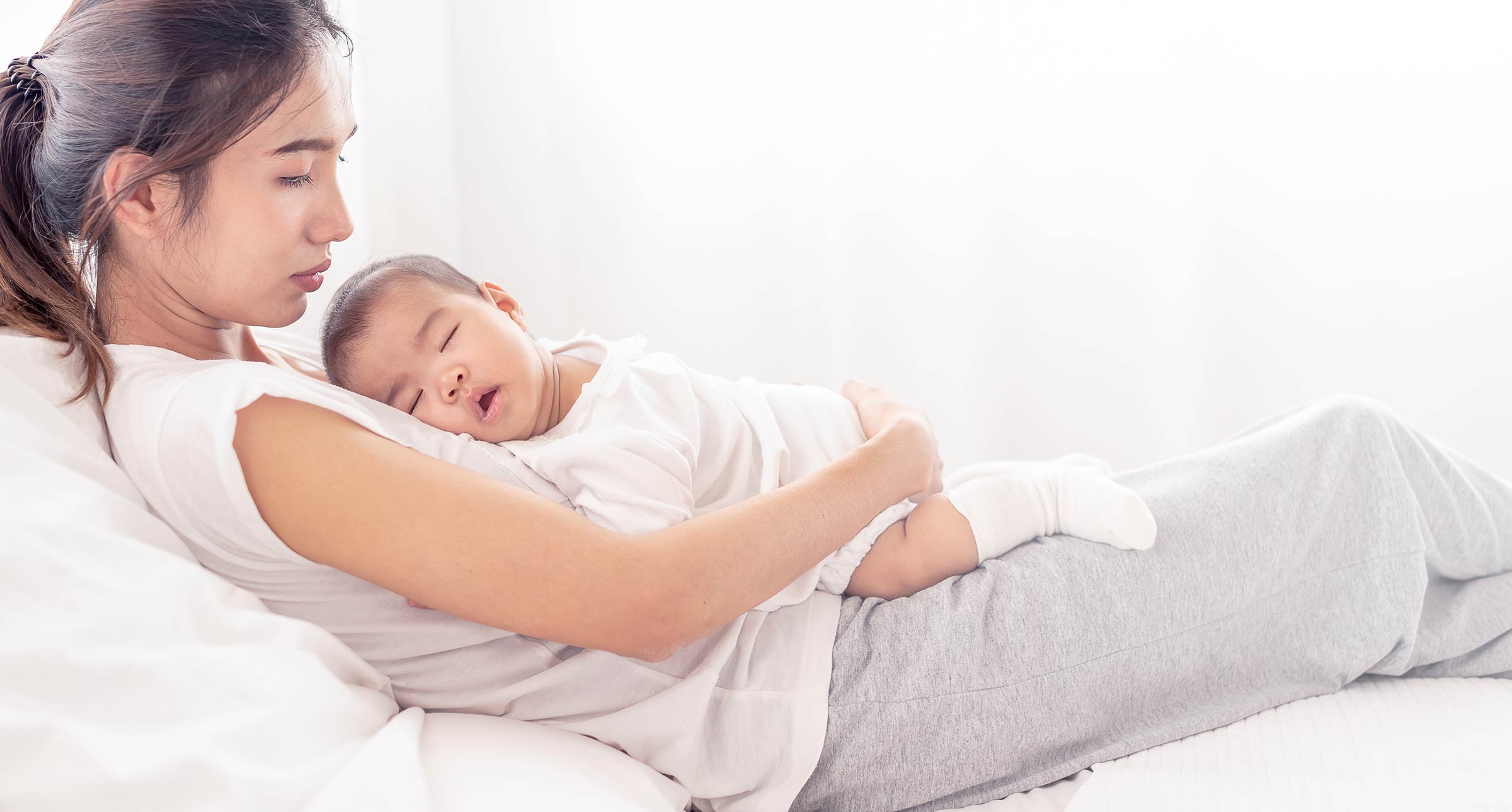
Breastfeeding has many benefits
Many new parents choose to breastfeed or chest feed their babies. The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding or chestfeeding until six months of age with ongoing breastfeeding and solid food introduction up to 2 years of age or longer. Per the WHO, new parents should be encouraged to offer breast milk to their children for at least the first year of life.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (APA), the Canadian Pediatric Society, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Centers for Disease Control urge parents to offer breast milk to their newborn babies.
While some parents are not able to offer breast milk or choose not to, science does demonstrate big benefits of breastfeeding for child health compared to formula-fed infants. In addition, research reveals the significant positive effects of breastfeeding on a new parent’s emotional and physical health.
Breast milk is a complete diet with all the necessary fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals in suitable proportions required for proper baby growth. In addition, breastfed infants have been shown to have greater immunity and therefore less illness. Breast milk is fresh, easily digested, and is a nutrient-rich food that can digest quickly.
Breastfeeding Benefits for Babies
Complete Nutritional Diet
Breast milk contains nutrients that babies require in different spans of their lives. In the early days after birth, breast milk has a thick yellowish consistency and is called colostrum. Colostrum is low in sugar and high in proteins necessary for lung maturation. As time passes, milk quantity changes to meet the baby’s changing dietary and health needs.
Exclusive breastfeeding is especially effective to help premature babies grow and develop naturally. Premature babies that breastfeed exclusively will benefit greatly from the nutrients in colostrum.

Boosting Immune System with Food
In the earlier days after birth, a baby’s immune system is not robust and ultimately depends on the passage of the birth parent’s immunity. Research shows that breast milk contains a considerable amount of antibody IgA and transfers from the feeding parent to baby.
This antibody helps a baby fight infection and forms a protective layer along the baby’s ‘mucosal membranes,’ from mouth to intestine, and in the nose, ears, and eyes and protects the baby from different diseases including heart disease and respiratory illnesses.
Interestingly, research also shows that babies fed human breast milk better respond to routine vaccines than babies that are not fed human milk.
Reduced Risk of Diseases
Different scientific findings show that exclusively breastfed babies are less prone to various diseases than babies fed only infant formula. Examples include:
- Lower risk of childhood obesity or Type-II diabetes later in life.
- Lower risk of respiratory illness such as respiratory tract infections and chronic lung disease.
- Fewer instances of intestinal ailments like diarrhea, constipation, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
- Reducing the baby’s risk of skin conditions, infections, high blood pressure, and allergies.
- Reducing the risk of childhood leukemia.
Socio-Behavioral Benefits
Ruth A. Lawrence, an infant-nutrition expert, reveals some startling stats about the benefits of breastfeeding in her book “Breastfeeding: A Guide for the Medical Profession.” She quoted research that exclusively breastfed babies have high intellectual capabilities later in life compared to formula-fed babies. Prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding is great for your baby’s brain development.
In addition, her research showed that breast milk-fed babies are five times less likely to suffer from eye and ear infections. There have been countless studies demonstrating the same benefits and others that show less of a difference between breast and formula-fed babies.
Breast Milk Vs. Alternatives
Breastfed babies are generally healthier than babies fed formula or cow’s milk. A baby’s body is very delicate and must be given proper nutrition in order to grow normally. Cow’s milk has very high cholesterol and has been linked to rheumatoid arthritis, which can even develop in young children.
It is important to create a smooth transition from breastfeeding to solid foods. Many mothers are not sure when to stop breastfeeding and start giving their baby mature milk and solid foods. Make sure you seek trustworthy health information from professionals who are licensed to provide medical advice.
Reduced Risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
The cause of SIDS is yet unknown, but research suggests that giving your baby breast milk during night feedings may reduce the chance of this tragedy.
Breastfeeding Benefits for Women’s Health
Cancer Prevention
These days, the rate of breast and ovarian cancer cases is increasing significantly. However, studies demonstrate a 5-15% decreased risk of developing these cancers in breastfeeding moms.
Breast Feeding Weight Loss
Research shows the fat-burning process in breastfeeding individuals is significantly higher than formula-feeding parents. Breastfeeding helps a person burn around 500 extra calories per day due to milk production.
Contraction of the Uterus
The pre-pregnancy size of the human uterus is usually equated to the size of a pear, which gradually expands during pregnancy. After the delivery, the uterus goes through a contraction process called ‘involution.’ One of the benefits of breastfeeding is the high level of oxytocin in the birth parent’s blood. This hormone plays a primary role in uterine contraction, and offering breast milk will help the uterus return to normal size. Research also indicates the reduced postpartum blood loss in new parents who start breastfeeding few hours after the birth.
Emotional Support for Breastfed Babies
Breastfeeding not only includes these physical and health benefits but also strengthens the parent-child emotional connection. The physical intimacy experienced as the baby nurses create a prolactin and serotonin surge in the parent’s and child’s bodies. The hormones released during a nursing session are essential for creating positive feelings and soothing and calmness.
Increased physical contact between parents and breastfed babies can help prevent postpartum depression.
Delayed Return to Menstruation
A high level of prolactin present in the blood ensures the sufficient production of breast milk. This high level of prolactin can help keep estrogen and progesterone hormone levels low. As these two hormones are responsible for ovulation in normal conditions, some breastfeeding individuals will have delayed returns of their menstrual cycles.
This is not true of all new parents, so be sure to discuss it with your healthcare provider should you wish to prevent another pregnancy during this time. Some people are able to get pregnant very soon after delivery, while some cannot get pregnant again as long as they are offering breast milk.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
What are some benefits of giving my baby breast milk?
Benefits of breastfeeding include health benefits to the baby and mom. Human milk provides a complete nutritional source and can help boost the immune system. As a result, breast milk feeding can decrease the risk of infections in babies and may even lead to advanced brain development.
What are some benefits of breastfeeding for moms?
Breastfeeding benefits for mom include helping the uterus contract, decreased risk of certain cancers, weight loss, and delayed menstruation for some.
With whom should I discuss my difficulties with breastfeeding?
Please discuss any feeding challenges with your physician and international board-certified lactation consultant.